基于时间轮算法实现的定时任务管理
最近在做车联网车辆远程诊断平台,发现平台与TBOX终端通信时需要保持一个心跳机制,与普通的由客户端发起,平台端ack的模式不一样的是本次心跳需要由平台端主动保持,即平台端每隔几秒发送一次心跳到终端设备,正常来说一般采用Java自带的Timer做一个定时即可,但是考虑到终端设备量级过高,在平台保存大量Timer实例对于平台的资源占用会非常多,造成性能低下的问题,于是决定采用时间轮算法的思路来解决这个海量定时器的方案。
算法说明
时间轮是一种高效来利用线程资源来进行批量化调度的一种调度模型。把大批量的调度任务全部都绑定到同一个的调度器上面,使用这一个调度器来进行所有任务的管理(manager),触发(trigger)以及运行(runnable)。能够高效的管理各种延时任务,周期任务,通知任务等等。
这个算法广泛运用于netty,kafka,akka等需要使用boss/work这种调度线程和工作线程隔离的模式架构中,在我的理解中,就是将原来的每一个Timer实例,作为一个每秒执行,或者每微秒执行的定时器,然后将需要执行的task全部绑定在每个时间刻度上,一旦当定时器执行到该刻度,即可以触发当前刻度上的所有task,利用这种方式节约Timer实例的资源消耗。
算法原理
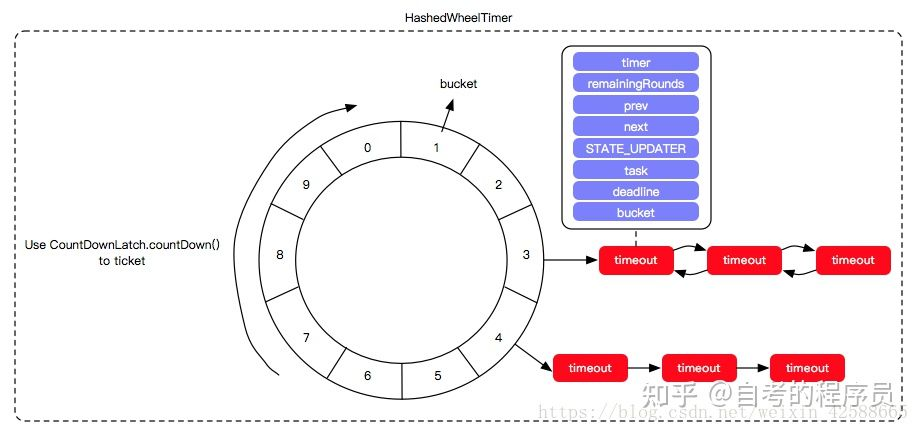
时间轮算法可以通过上图来描述。假设时间轮大小为10,1s转一格,每格指向一个链表,保存着待执行的任务。
假设,当前位于1,现在要添加一个3s后指向的任务,则1+3=4,在第4格的链表中添加一个节点指向任务即可,标识round=0(round表示圈数)。
假设,当前位于1,现在要添加一个10s后指向的任务,则(1+10)% 10 = 1,则在第1格添加一个节点指向任务,并标识round=1(round表示圈数),则当时间轮第二次经过第1格时,即会执行任务。
时间轮只会执行round=0的任务,并会把该格子上的其他任务的round减1。
Q:为什么时间段是一个圆形?采用环形链表?
A:之所以使用环形的数据结构,主要是处理时间跨度很大的问题。假如我们1s是一个时间段,一天24小时,我们需要划分246060=86400个区间,如果是1个月呢。显然环形结构可以很优雅的处理该问题。
如图我们认为这是一个周期为12秒的圆形,每个数字间隔是1s。我们要表示60s就是60/12=5。也就是指针从12开始转5圈。由此可见,一个圆形可以处理任何时间跨度。
算法实现
代码结构
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13com.gladium.timer
├── Timer // Timer实例接口
├── TimerTask // task定义父类
├── TimingWheel // 时间调度及队列处理
├── TimerTaskEntry // task定时信息
├── TimerTaskList // task列表管理
├── CancelCallBackTask // task退出执行的任务定义父类
├── impl
│ └── TimerImpl // Timer实现类,管理boss/task线程池
├── biz // 业务处理
│ └── HeartBeatTask // 心跳业务(需要循环的业务主类)
│ └── ReturnControllerCallBackTask // 归还连接(task超时退出时执行检查)
│ └── TimerWheelPool // 业务管控(包含有循环中断,续期等业务封装)代码实现
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30package com.gladium.timer;
public interface Timer {
/**
* 增加一个延迟任务
* @param task
*/
void add(TimerTask task);
/**
* 调整时间轮
* @param timeout
* @return
* @throws InterruptedException
*/
boolean advanceClock(long timeout) throws InterruptedException;
/**
* @return 当前任务数量
*/
int size();
/**
* 关闭时间轮
*/
void shutdown();
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84package com.gladium.timer;
public abstract class TimerTask implements Runnable {
/** 延时时间 */
long delayTime;
/** 任务运行主类 */
private TimerTaskEntry timerTaskEntry;
/** 退出回调运行主类 */
private CancelCallBackTask callBackTask;
/** 最长运行时间 默认10分钟 */
long maxTime = 10 * 60 * 1000;
/** 是否是循环任务 默认否 */
boolean isCycle = false;
public TimerTask(long delayTime) {
this.delayTime = delayTime;
}
public TimerTask(long delayTime, long maxTime) {
this.delayTime = delayTime;
this.maxTime = maxTime;
}
public TimerTask(long delayTime, long maxTime, boolean isCycle) {
this.delayTime = delayTime;
this.maxTime = maxTime;
this.isCycle = isCycle;
}
public TimerTask(long delayTime, long maxTime, boolean isCycle,CancelCallBackTask callBackTask) {
this.delayTime = delayTime;
this.maxTime = maxTime;
this.isCycle = isCycle;
this.callBackTask = callBackTask;
}
/**
* @description: 直接调用当前对象的退出
* @param:
* @return: void
* @date: Create in 2022/9/8 9:43
*/
public synchronized void cancel() {
if (timerTaskEntry != null) {
timerTaskEntry.remove();
}
timerTaskEntry = null;
}
/**
* @description: 调用子类的判断方法 用于判断当前任务是否结束
* @return: boolean
* @date: Create in 2022/9/8 9:43
*/
protected abstract boolean isCancel();
/**
* @description: 调用子类的超时时间续期,用于判断是否重置超时时间
* @return: boolean
* @date: Create in 2022/9/8 9:43
*/
protected abstract void checkTimeOut();
public TimerTaskEntry getTimerTaskEntry() {
return timerTaskEntry;
}
public synchronized void setTimerTaskEntry(TimerTaskEntry entry) {
// if this timerTask is already held by an existing timer task entry,
// we will remove such an entry first.
if (timerTaskEntry != null && timerTaskEntry != entry) {
timerTaskEntry.remove();
}
timerTaskEntry = entry;
this.timerTaskEntry = timerTaskEntry;
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97package com.gladium.timer;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
public class TimingWheel {
private long tickMs;
private int wheelSize;
private long interval;
private long startMs;
private AtomicInteger taskCounter;
private DelayQueue queue;
private long currentTime;
private TimerTaskList[] buckets;
private volatile TimingWheel overflowWheel;
/**
* @param tickMs 轮子每个格子的时间
* @param wheelSize 每个轮子的大小
* @param startMs 开始时间
* @param taskCounter 任务计数器
* @param queue 延迟队列
*/
public TimingWheel(long tickMs, int wheelSize, long startMs, AtomicInteger taskCounter, DelayQueue queue) {
this.tickMs = tickMs;
this.wheelSize = wheelSize;
this.interval = tickMs * wheelSize;
this.startMs = startMs;
this.taskCounter = taskCounter;
this.queue = queue;
this.currentTime = startMs - (startMs % tickMs);
buckets = new TimerTaskList[wheelSize];
for (int i = 0; i < wheelSize; i++) {
buckets[i] = new TimerTaskList(taskCounter);
}
}
/**
* 增加一个上层时间轮
*/
private void addOverflowWheel() {
synchronized (this) {
if (overflowWheel == null) {
overflowWheel = new TimingWheel(interval, wheelSize, startMs, taskCounter, queue);
}
}
}
/**
* 添加任务
* @param timerTaskEntry
* @return
*/
public boolean add(TimerTaskEntry timerTaskEntry) {
long expiration = timerTaskEntry.expirationMs;
boolean res = false;
if (timerTaskEntry.cancelled()) {
return false;
} else if (expiration < currentTime + tickMs) {
return false;
} else if (expiration < currentTime + interval) {
long virtualId = expiration / tickMs;
int index = (int) (virtualId % wheelSize);
TimerTaskList bucket = buckets[index];
bucket.add(timerTaskEntry);
if (bucket.setExpiration(virtualId * tickMs)) {
queue.offer(bucket);
}
return true;
} else {
if (overflowWheel == null) {
addOverflowWheel();
}
overflowWheel.add(timerTaskEntry);
return true;
}
}
/**
* 时间推进
* @param timeMs
*/
public void advanceClock(long timeMs) {
if (timeMs >= currentTime + tickMs) {
currentTime = timeMs - (timeMs % tickMs);
// Try to advance the clock of the overflow wheel if present
if (overflowWheel != null) {
overflowWheel.advanceClock(currentTime);
}
}
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80package com.gladium.timer;
import java.util.Optional;
public class TimerTaskEntry {
TimerTask timerTask;
long expirationMs;
long firstExecuteTime;
volatile TimerTaskList list;
TimerTaskEntry next;
TimerTaskEntry prev;
public TimerTaskEntry(TimerTask timerTask, long expirationMs) {
this.timerTask = timerTask;
this.expirationMs = expirationMs;
if(this.firstExecuteTime == 0){
// 在循环时继承之前的首次执行时间
setFirstExecuteTime(Optional.ofNullable(timerTask).map(TimerTask::getTimerTaskEntry).map(TimerTaskEntry::getFirstExecuteTime).filter(p -> p != 0).orElse(expirationMs));
}
if (timerTask != null) {
timerTask.setTimerTaskEntry(this);
}
}
// 重置开始执行时间 为了重置超时时间
public synchronized void renewFirstExecuteTime(long firstExecuteTime){
this.firstExecuteTime = firstExecuteTime;
}
public synchronized void setFirstExecuteTime(long firstExecuteTime){
if(this.firstExecuteTime == 0){
this.firstExecuteTime = firstExecuteTime;
}
}
public boolean cancelled() {
return timerTask.getTimerTaskEntry() != this || timerTask.isCancel();
}
// 是否超过最大的超时时间
public boolean isTimeOut(){
// 每次均执行超时检查,主要是调用子类的方法,对超时策略进行修改
timerTask.checkTimeOut();
return firstExecuteTime != 0 && ((firstExecuteTime + timerTask.getMaxTime() - timerTask.getDelayTime()) <= System.currentTimeMillis());
}
// 是否执行callback
public boolean isExecuteCallBack(){
return timerTask.getCallBackTask().isExecute();
}
public void remove() {
TimerTaskList currentList = list;
// If remove is called when another thread is moving the entry from a task entry list to another,
// this may fail to remove the entry due to the change of value of list. Thus, we retry until the list becomes null.
// In a rare case, this thread sees null and exits the loop, but the other thread insert the entry to another list later.
while (currentList != null) {
currentList.remove(this);
currentList = list;
}
}
public TimerTask getTimerTask() {
return timerTask;
}
public void setTimerTask(TimerTask timerTask) {
this.timerTask = timerTask;
}
public long getFirstExecuteTime() {
return firstExecuteTime;
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84package com.gladium.timer;
import java.util.concurrent.Delayed;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicLong;
public class TimerTaskList implements Delayed {
private TimerTaskEntry root = new TimerTaskEntry(null, -1L);
private AtomicLong expiration = new AtomicLong(-1L);
private AtomicInteger taskCounter;
public TimerTaskList(AtomicInteger taskCounter) {
root.prev = root;
root.next = root;
this.taskCounter = taskCounter;
}
public void add(TimerTaskEntry timerTaskEntry) {
boolean done = false;
while (!done) {
timerTaskEntry.remove();
synchronized(this) {
if (timerTaskEntry.list == null) {
TimerTaskEntry tail = root.prev;
timerTaskEntry.next = root;
timerTaskEntry.prev = tail;
timerTaskEntry.list = this;
tail.next = timerTaskEntry;
root.prev = timerTaskEntry;
taskCounter.incrementAndGet();
done = true;
}
}
}
}
public boolean setExpiration(long expirationMs) {
return expiration.getAndSet(expirationMs) != expirationMs;
}
public long getExpiration() {
return expiration.get();
}
public void remove(TimerTaskEntry timerTaskEntry) {
synchronized(this) {
if (timerTaskEntry.list.equals(this)) {
timerTaskEntry.next.prev = timerTaskEntry.prev;
timerTaskEntry.prev.next = timerTaskEntry.next;
timerTaskEntry.next = null;
timerTaskEntry.prev = null;
timerTaskEntry.list = null;
taskCounter.decrementAndGet();
}
}
}
public synchronized void flush(Consumer<TimerTaskEntry> flush) {
TimerTaskEntry head = root.next;
while(!head.equals(root)) {
remove(head);
flush.accept(head);
head = root.next;
}
expiration.set(-1L);
}
public long getDelay(TimeUnit unit) {
return Math.max(0, unit.convert(expiration.get() - System.currentTimeMillis(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS));
}
public int compareTo(Delayed o) {
if (o instanceof TimerTaskList) {
return Long.compare(expiration.get(), ((TimerTaskList) o).getExpiration());
}
return 0;
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17package com.gladium.timer;
/**
* @description: 任务退出后回调方法
* @date Create in 2022/9/9 15:56
*/
public abstract class CancelCallBackTask implements Runnable{
/**
* @description: 是否可以执行
* @return: boolean
* @date: Create in 2022/9/9 15:58
*/
protected abstract boolean isExecute();
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107package com.gladium.timer.impl;
import com.gladium.timer.*;
import java.util.Optional;
import java.util.concurrent.DelayQueue;
import java.util.concurrent.ExecutorService;
import java.util.concurrent.Executors;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
import java.util.concurrent.atomic.AtomicInteger;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.Lock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReadWriteLock;
import java.util.concurrent.locks.ReentrantReadWriteLock;
/**
* @description: 时间轮实现类
* @date: Create in 2022/9/9 16:34
*/
public class TimerImpl implements Timer {
private ExecutorService taskExecutor;
private ExecutorService bossExecutor;
private DelayQueue<TimerTaskList> delayQueue = new DelayQueue<>();
private AtomicInteger taskCounter = new AtomicInteger();
private TimingWheel timingWheel;
private ReadWriteLock readWriteLock = new ReentrantReadWriteLock();
private Lock readLock = readWriteLock.readLock();
private Lock writeLock = readWriteLock.writeLock();
public TimerImpl(long tickMs, int wheelSize, long pollInterval) {
timingWheel = new TimingWheel(tickMs, wheelSize, System.currentTimeMillis(), taskCounter, delayQueue);
taskExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(100);
bossExecutor = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(1);
bossExecutor.submit((Runnable) () -> {
while (true) {
try {
advanceClock(pollInterval);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
});
}
public void add(TimerTask task) {
readLock.lock();
try {
addTimerTaskEntry(new TimerTaskEntry(task, task.getDelayTime() + System.currentTimeMillis()));
} finally {
readLock.unlock();
}
}
private void addTimerTaskEntry(TimerTaskEntry timerTaskEntry) {
if (!timingWheel.add(timerTaskEntry)) {
// 校验任务是否退出 校验任务是否超时
if ((!timerTaskEntry.cancelled()) && (!timerTaskEntry.isTimeOut())) {
taskExecutor.submit(timerTaskEntry.getTimerTask());
// 循环任务,则继续提交到下一个时间刻度
if(timerTaskEntry.getTimerTask().isCycle()){
add(timerTaskEntry.getTimerTask());
}
}else {
CancelCallBackTask cancelCallBackTask = Optional.ofNullable(timerTaskEntry).map(TimerTaskEntry::getTimerTask).map(TimerTask::getCallBackTask).orElse(null);
// 执行最后数据结束后的回调方法 中途打断后 无法执行后续回调
if(cancelCallBackTask != null && timerTaskEntry != null && timerTaskEntry.isExecuteCallBack()){
taskExecutor.submit(cancelCallBackTask);
}
}
}
}
public boolean advanceClock(long timeout) throws InterruptedException {
TimerTaskList bucket = delayQueue.poll(timeout, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
boolean res;
if (bucket != null) {
try {
writeLock.lock();
while (bucket != null) {
timingWheel.advanceClock(bucket.getExpiration());
bucket.flush(this::addTimerTaskEntry);
bucket = delayQueue.poll();
}
} finally {
writeLock.unlock();
}
return true;
} else {
return false;
}
}
public int size() {
return taskCounter.get();
}
public void shutdown() {
taskExecutor.shutdown();
bossExecutor.shutdown();
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58package com.gladium.timer.biz;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.concurrent.TimeUnit;
/**
* @description: 心跳定时任务
* @date Create in 2022/9/8 13:28
*/
public class HeartBeatTask extends TimerTask {
static DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
private HeartBeatTask(){
// 默认实例化父类
super(DELAY_TIME,MAX_TIME,IS_CYCLE);
}
/**
* @description: 构建任务对象
* @date: Create in 2022/9/8 13:51
*/
public HeartBeatTask(CancelCallBackTask callBackTask){
super(DELAY_TIME,MAX_TIME,IS_CYCLE,callBackTask);
}
public void run() {
// 在此处完成具体需执行任务
System.out.println(dtf.format(LocalDateTime.now()) +" 发送心跳");
}
protected boolean isCancel() {
// 可以采用监听公共类,redis等唯一信息判断true/false
return false;
}
protected void checkTimeOut() {
// 根据情况,执行重置超时时间
this.getTimerTaskEntry().renewFirstExecuteTime(System.currentTimeMillis());
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43package com.gladium.timer.biz;
import com.google.common.collect.Lists;
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
import org.springframework.kafka.core.KafkaTemplate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.List;
/**
* @description: 归还控制权限 心跳任务结束后执行
* @date Create in 2022/9/9 16:35
*/
public class ReturnControllerCallBackTask extends CancelCallBackTask {
public ReturnControllerCallBackTask(){
}
protected boolean isExecute() {
// 通过监听公共类,redis等数据,校验是否执行循环结束后回调
// 该校验只会执行一次
return true;
}
public void run() {
// 在此处完成循环结束后需要完成的任务
System.out.println(dtf.format(LocalDateTime.now()) +" 默认回调发送归还控制");
}
}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53package com.gladium.timer.biz;
/**
* @description: 时间轮定时任务池
* @date Create in 2022/9/8 14:25
*/
public class TimerWheelPool {
private static Timer timer= null;
/**
* @description: 新增任务
* @param: timerTask
* @return: void
* @date: Create in 2022/9/8 14:29
*/
public static void addTask(TimerTask timerTask){
if(timer == null){
timer = new TimerImpl(1000, 10, 5000);
}
timer.add(timerTask);
}
/**
* @description: 获取当前任务量
* @param:
* @return: int
* @date: Create in 2022/9/8 14:30
*/
public static int size(){
return timer == null?0:timer.size();
}
/**
* @description: 退出任务 需要校验是否完成 等任务
* @return: void
* @date: Create in 2022/9/8 14:33
*/
public static void cancelTask(){
new HeartBeatTask().addCancelTask();
}
/**
* @description: 续期任务 回调完成 归还控制 等任务
* @return: void
* @date: Create in 2022/9/8 14:33
*/
public static void renewTask(){
new HeartBeatTask().addRenewTask();
}
}
总结
时间轮算法的高效的管理和较低的资源占用使得此算法成为众多高吞吐,高并发框架的首选,但时间轮算法亦有其弊端:
精度取决于每一格精度,精度越小误差越小,当随之而来的,精度越小,所能承载的任务时间跨度就越小,即使使用分层时间论,但是层次的切换也会使得效率大打折扣。
时间轮无法备份,当服务器宕机时会丢失所有任务。
分布式情况下,会出现任务分配不均的问题,同时也无法合理的分配资源和任务的比重。